LncRRIsearch provides users following three types of search methods.
Explanations of search result page
Limitations of RIblast predictions
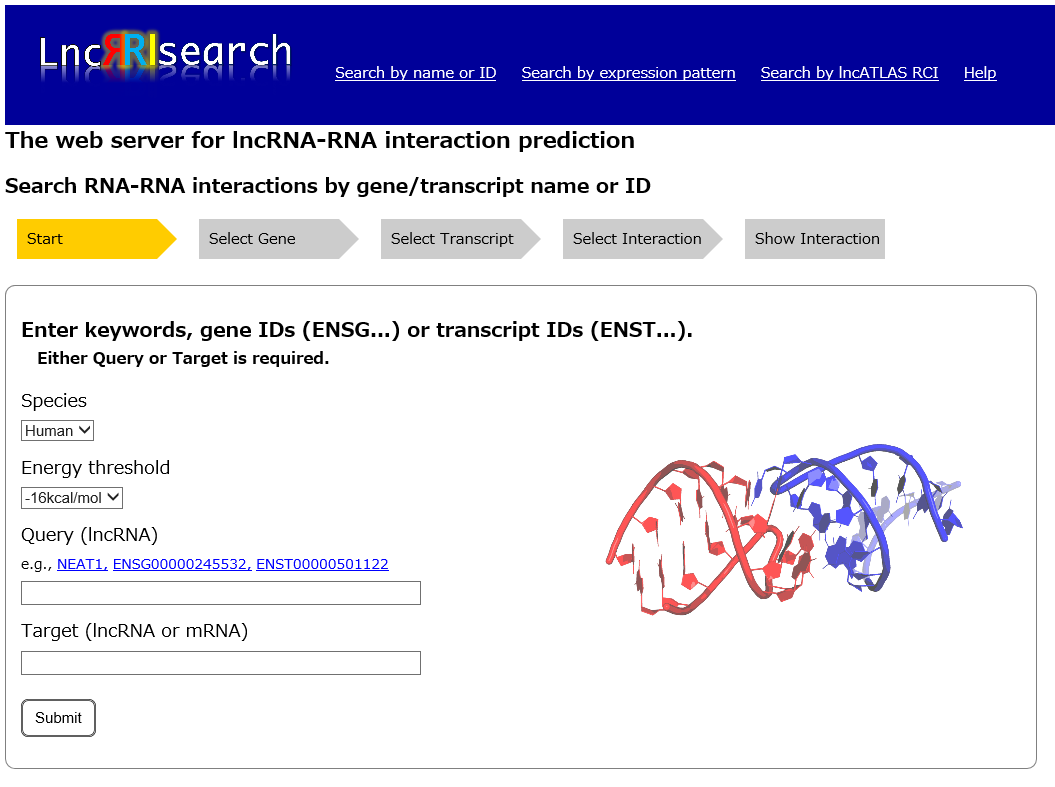
Search for RNA-RNA interaction based on gene/transcript name or ID
|
Step1:
Two RNA transcripts (Query lncRNA and Target RNA) are needed to be specified by users for searching an arbitrary RNA-RNA interaction of interest. Currently GENCODE gene/transcript names or IDs are supported as the input query.
Species: Human or Mouse data is currently available in LncRRIsearch.
Energy threshold: threshold of the local base-pairing interaction energy calculated by RIblast.
|
|
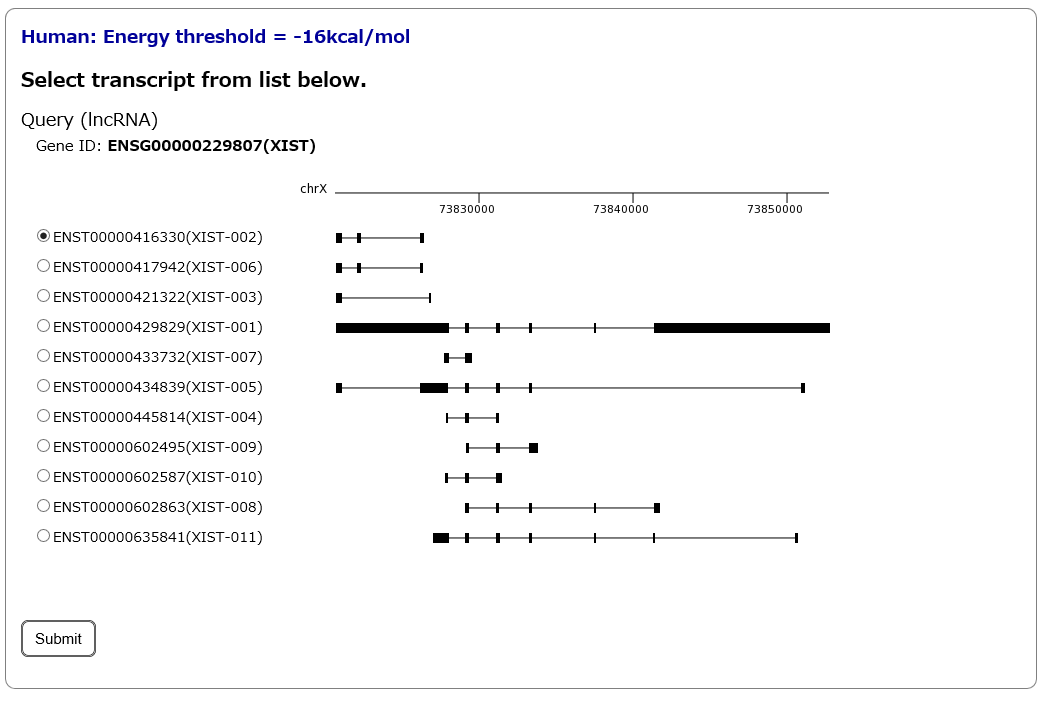
Step2:
Several transcript isoforms encoded by the gene will be listed, when users input the gene name or ID. Among these isoforms, users can select a single isoform of interest.
# This page will be skipped, if users specify a single query transcript in Step1, or if the gene encodes only a single transcript.
|
|
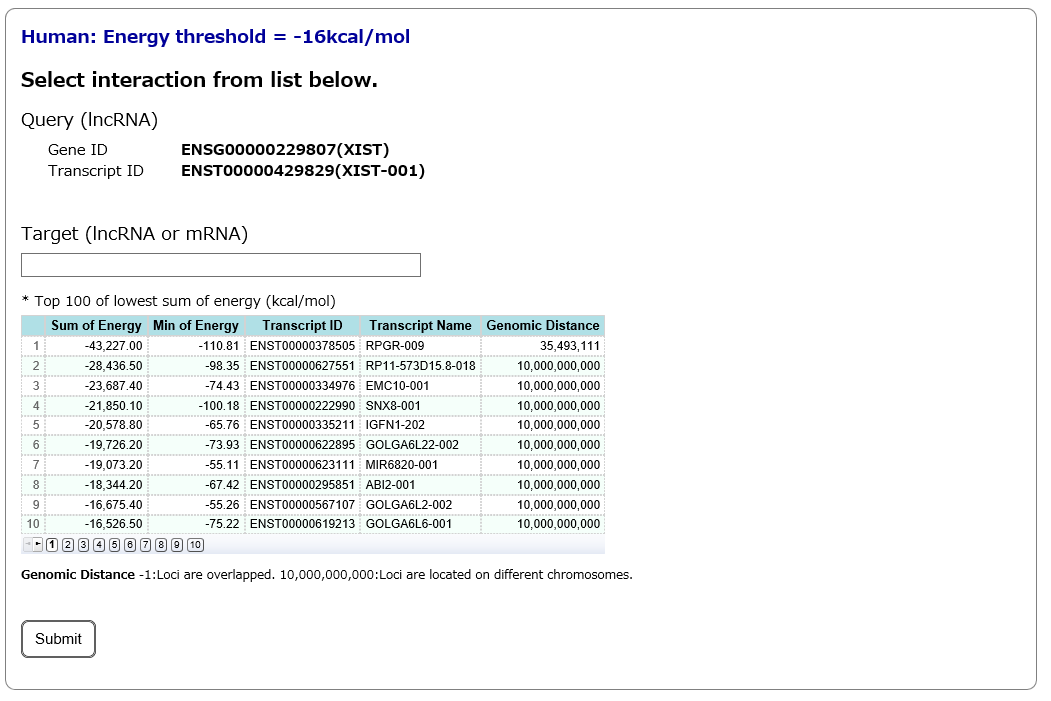
Step3:
After specifying the lncRNA transcript (query) in Step2, all interacting RNAs (target lncRNAs and mRNAs) predicted by RIblast are listed. Among these target RNAs, users can select a target RNA of interest.
# This page will be skipped, if users specify both query and target RNAs in Step1.
|
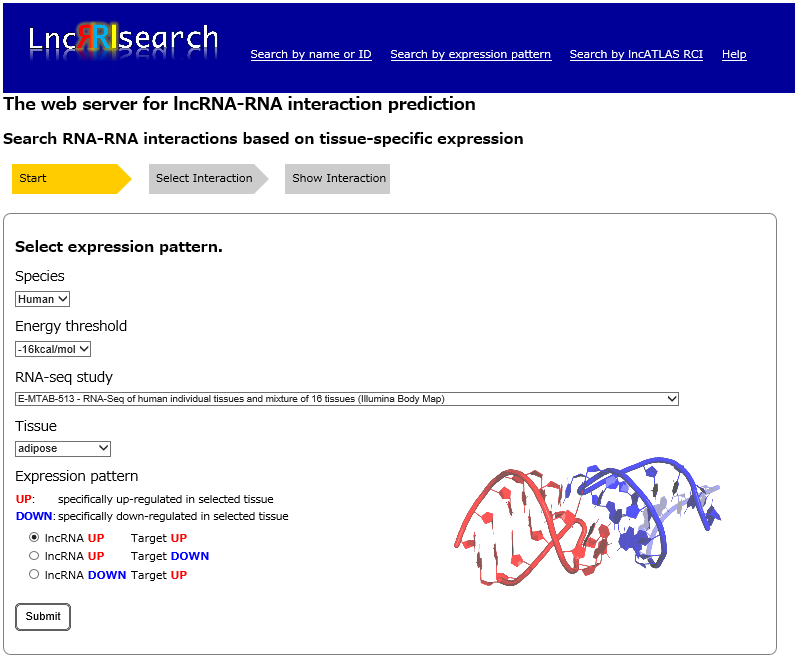
Search for tissue-specific RNA-RNA interaction
Tissue-specific RNA-RNA interactions involving lncRNAs and their target RNAs exhibiting tissue-specific expression patterns can be searched in LncRRIsearch.
|
Step1:
An RNA-seq dataset from four different RNA-seq studies, and a tissue of interest are needed to be selected. For the selected tissue, three possible scenarios of tissue-specific expression patterns of query and target RNA transcripts should be selected.
- Query and target RNAs are specifically up-regulated in the same tissue.
- Query RNAs are specifically up-regulated and target RNAs are down-regulated in the same tissue.
- Query RNAs are specifically down-regulated and target RNAs are up-regulated in the same tissue.
Species: Human or Mouse data is currently available in LncRRIsearch.
Energy threshold: threshold of the local base-pairing interaction energy calculated by RIblast.
|
|
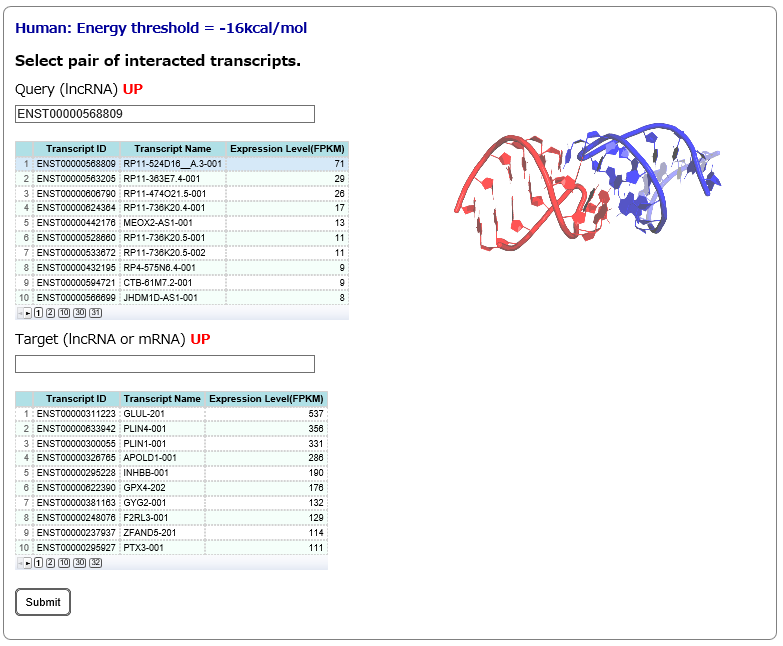
Step2:
After selecting the scenarios of tissue-specific expression patterns of query and target RNAs in Step1, the corresponding query and target RNAs are listed. In this page, once a query RNA is selected, the list of target RNAs (interactions predicted by RIblast) is automatically updated for the selected query. In this step, query(lncRNA) and target(lncRNA or mRNA) are needed to be selected.
|
Search for RNA-RNA interaction based on subcellular localization
In LncRRIsearch, RNA-RNA interactions can be searched based on subcellular localization of lncRNAs and their target RNAs.
|
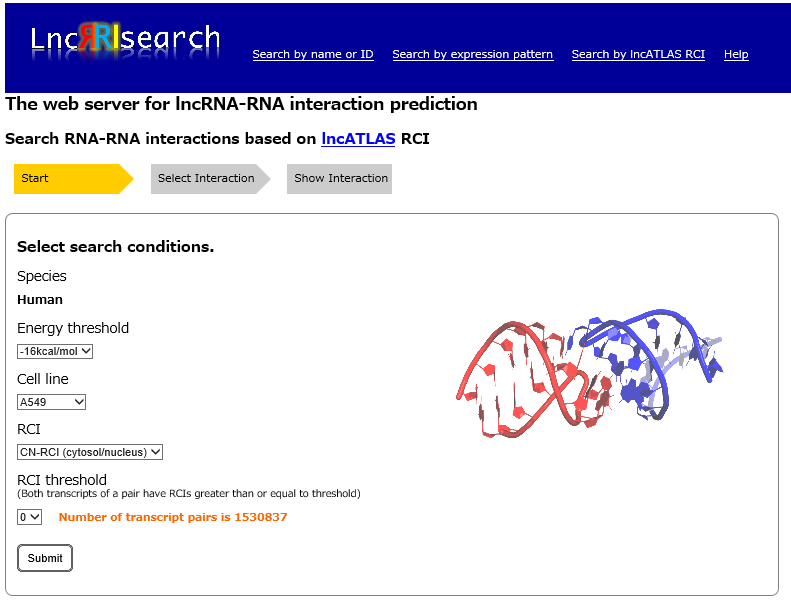
Step1:
Main subcellular location of lncRNAs and their target RNAs can be specified by selecting cell line name, type of RCI, RCI threshold. In the RCI types, CN-RCI(cytosol/nucleus) is useful for searching cytoplasmic RNAs, and NC-RCI(nucleus/cytosol) is useful for searching nuclear RNAs..
RCI(Relative Concentration Index): Index of subcellular localization of RNA transcripts. Please see lncATLAS for the details.
Energy threshold: threshold of the local base-pairing interaction energy calculated by RIblast.
|
|
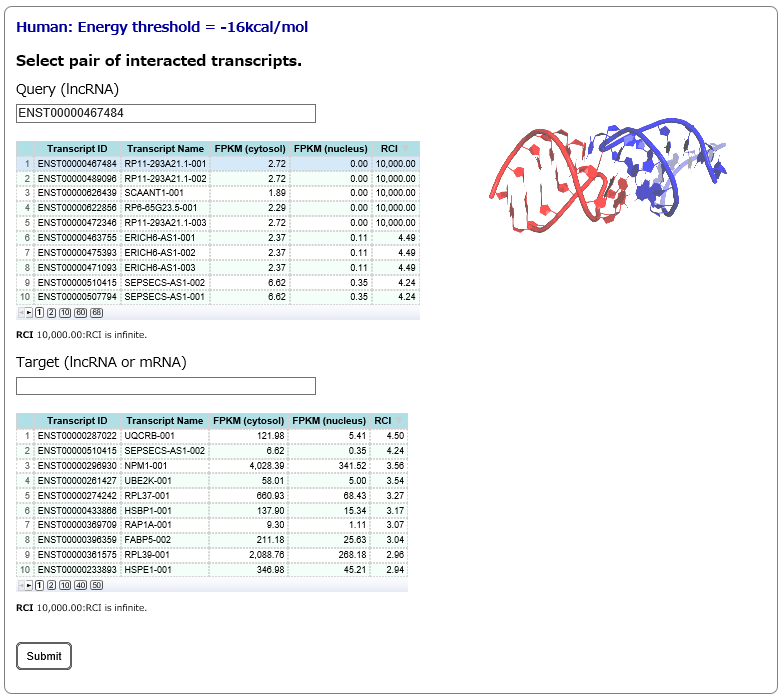
Step2:
After specifying a main subcellular location of query and target RNAs in Step1, the corresponding query and target RNAs are listed. In this page, once a query RNA is selected, the list of target RNAs (interactions predicted by RIblast) is automatically updated for the selected query. In this step, query(lncRNA) and target(lncRNA or mRNA) are needed to be selected.
RCI = 10,000.00 indicates the RNA transcripts were not detectable (0 FPKM in RNA-seq data) in one of two subcellular compartments.
|
Explanations of search result page
|
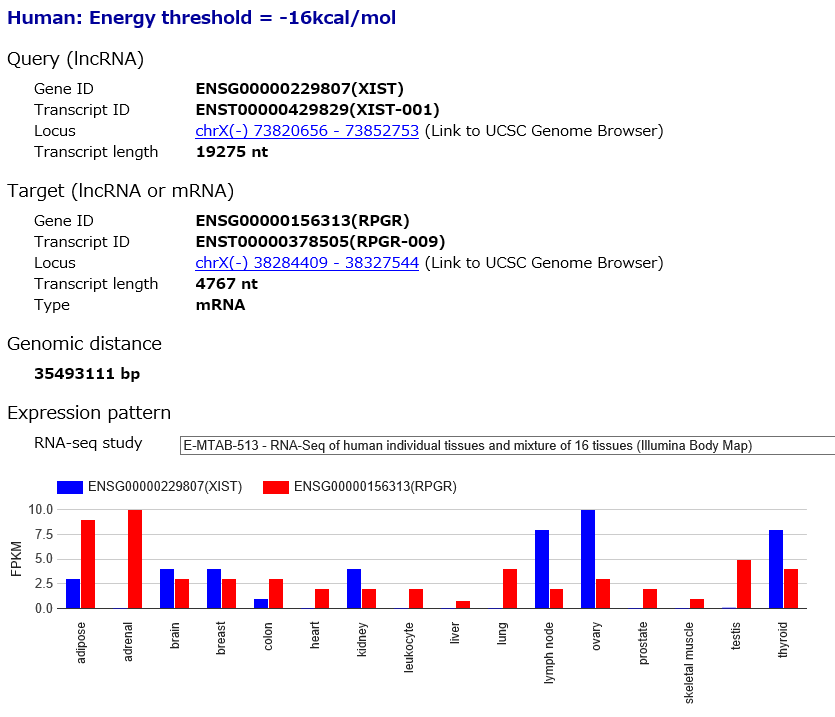
The details of base-pairing interaction between query and target transcripts are described.
Query (lncRNA) and Target (lncRNA or mRNA) indicate that the detailed information about the users' specified genes and transcripts.
Expression pattern shows expression levels of query and target RNAs across multiple human tissues. Users can select the expression pattern from following RNA-seq studies.
For human
- E-MTAB-2836: Human Protein Atlas Project (32 tissues)
- E-MTAB-2919: GTEx Consortium (30 tissues)
- E-MTAB-513: Human Body Map Project (16 tissues)
- E-MTAB-3871: Epigenome Roadmap Project (19 tissues)
- E-MTAB-3358: RIKEN FANTOM5 Project (56 tissues)
For mouse
- E-GEOD-74747: C57BL/6 strain (9 tissues)
- E-MTAB-2801-C57BL6: C57BL/6 strain (8 tissues)
- E-MTAB-2801-CD1: CD1 strain (9 tissues)
- E-MTAB-2801-DBA2J: DBA/2J strain (9 tissues)
|
|
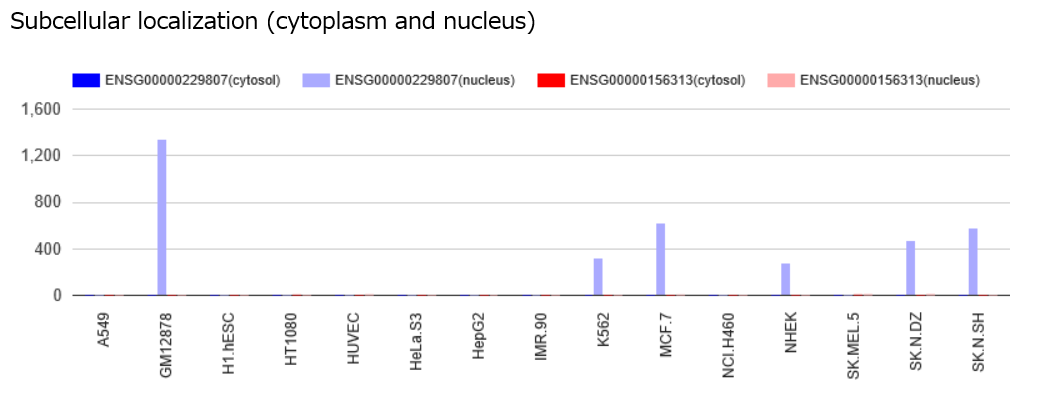
RNA-seq data for subcellular localization of query and target RNAs
|
|
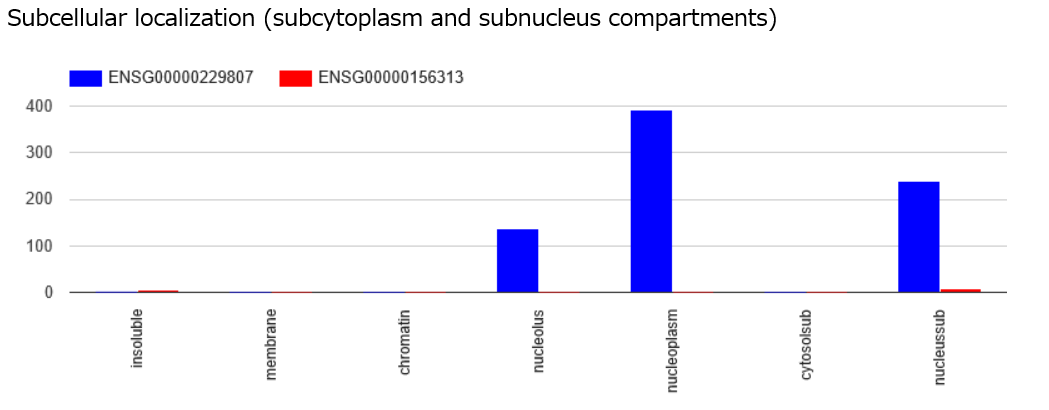
RNA-seq data of K562 cell line for subcellular localization of query and target RNAs
|

|
Global base-pairing interaction shows the several statistics of base-pairing interactions and a graphical view of all local base-pairing interactions between query and target RNAs. All interaction energies were calculated by RIblast.
Local base-pairing interactions (Top 10) show the text view of the ten most stable local base-pairing interactions between query and target RNAs predicted by RIblast.
|
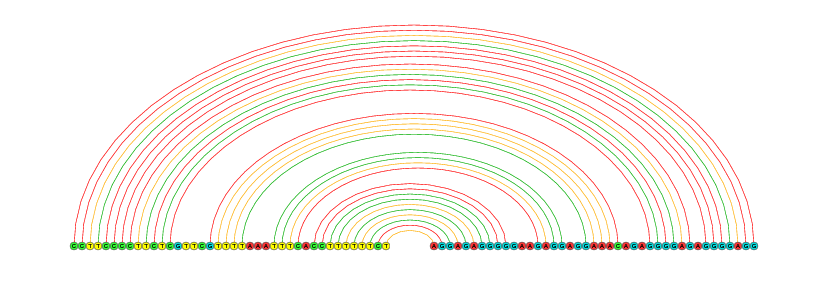
|
Create figure buttons provide the graphical representations of each local base-pairing interactions (visualized by VARNA).
|
Limitations of RIblast predictions
Although the lncRNA-RNA interaction prediction accuracy of RIblast is superior to that of existing approaches, our prediction results should still include many false-positive predictions. This is because RIblast did not consider complex structure folding such as RNA tertiary structures, non-canonical base-pairing and co-transcriptional folding process. The development of more accurate RNA-RNA interaction prediction programs is an important challenge in RNA bioinformatics. To reduce this limitation, LncRRIsearch includes tissue-specific expression information, which will enable users to evaluate the reliability of the predicted interactions.











